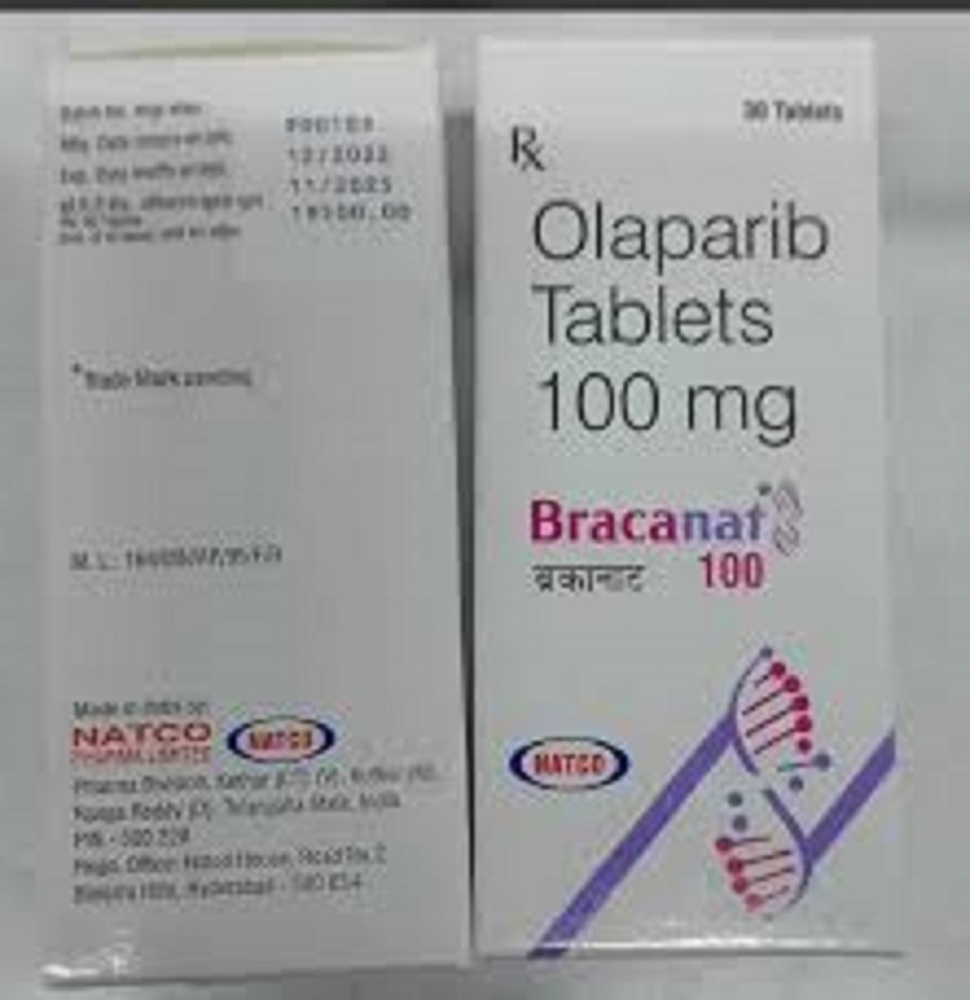
Bracanat 100 Mg Tablets
Product Details:
- Dosage Form Tablet
- Pacakaging (Quantity Per Box) 30 Tablets per Box
- Indication Ovarian Cancer, Fallopian Tube Cancer, Peritoneal Cancer
- Origin of Medicine India
- Salt Composition Niraparib Tosylate Monohydrate
- Drug Type Allopathic
- Ingredients Niraparib Tosylate Monohydrate (Equivalent to Niraparib 100 mg)
- Click to View more
Bracanat 100 Mg Tablets Price And Quantity
- 16000 INR/Bottle
- 1 Bottle
- White to off-white film-coated tablet
- Not to be used during pregnancy and lactation unless advised by the physician
- Nausea, fatigue, anemia, thrombocytopenia, constipation, insomnia
- Bracanat 100
- L01XX54
- Hypersensitivity to Niraparib or any excipients
- Oral
- 24 months
- Yes
- Natco Pharma Limited
Bracanat 100 Mg Tablets Product Specifications
- Anticancer (PARP Inhibitor)
- 30 Tablets
- Ovarian Cancer, Fallopian Tube Cancer, Peritoneal Cancer
- Take with or without food, as advised by doctor
- Tablet
- Adults
- 30 Tablets per Box
- Cancer Treatment (Ovarian Cancer, Fallopian Tube Cancer, Peritoneal Cancer)
- As directed by physician
- Niraparib Tosylate Monohydrate
- Niraparib Tosylate Monohydrate (Equivalent to Niraparib 100 mg)
- Store below 30C, Protect from light and moisture
- Tablets
- Allopathic
- India
- White to off-white film-coated tablet
- Not to be used during pregnancy and lactation unless advised by the physician
- Nausea, fatigue, anemia, thrombocytopenia, constipation, insomnia
- Bracanat 100
- L01XX54
- Hypersensitivity to Niraparib or any excipients
- Oral
- 24 months
- Yes
- Natco Pharma Limited
Product Description
Bracanat 100mg Tablet may be taken with or without food. Swallow the tablets whole, without crushing, chewing, or splitting them. Take it regularly and at the same time every day to maintain an even level of the medication in your body. Follow your doctors instructions on the exact dosage and schedule.
Common side effects include nausea, fatigue, vomiting, loss of appetite, diarrhea, and dizziness. If you experience nausea or vomiting, eating smaller, more frequent meals and staying hydrated can help. Inform your doctor if these side effects become severe or do not go away. Be cautious about driving or operating heavy machinery if you feel dizzy or fatigued.
While taking Bracanat 100mg Tablet, avoid consuming grapefruit or grapefruit juice as it can increase the risk of side effects. This medicine can cause harm to an unborn baby, so it is important to use effective contraception during treatment and for some time after the last dose. Inform your doctor if you are pregnant, planning to become pregnant, or breastfeeding. Regular blood tests are needed to monitor your blood cell counts and liver function during treatment. Do not start any new medications or supplements without consulting your doctor, as they may interact with Bracanat 100mg Tablet.
What is Bracanat 100 Mg and how does it work?
Bracanat 100 Mg is an anticancer tablet containing Niraparib Tosylate Monohydrate, primarily used in the treatment of ovarian, fallopian tube, and peritoneal cancers. As a PARP inhibitor, it works by targeting and inhibiting enzymes involved in the repair of DNA within cancer cells, leading to their destruction and preventing tumor growth.
Directions for Correct Usage
Bracanat 100 tablets are taken orally, either with or without food, as advised by your physician. The dosage should strictly follow your doctor's prescription to ensure optimal efficacy while minimizing potential side effects. Do not adjust the dose or stop taking the medication without consulting your healthcare provider.
Storage and Shelf Life Guidelines
For maximum effectiveness and safety, store Bracanat 100 tablets in their original packaging below 30C, protected from light and moisture. The product comes with a shelf life of 24 months, so always check the expiry date before use and keep out of reach of children.
FAQ's of Bracanat 100 Mg Tablets:
Q: How should Bracanat 100 Mg Tablets be taken for best results?
A: Take Bracanat 100 Mg Tablets orally, following your physician's prescribed dosage. You can administer the tablets with or without food. It is important to consistently take the medication at the same time each day for best outcomes.Q: What conditions are Bracanat 100 Mg Tablets recommended for?
A: Bracanat 100 Mg Tablets are indicated for the treatment of ovarian cancer, fallopian tube cancer, and peritoneal cancer in adults, under the supervision of a healthcare professional.Q: What should I do if I miss a dose of Bracanat 100 Mg?
A: If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember unless it is almost time for your next dose. Do not double up doses; simply continue with your regular schedule and inform your doctor if you frequently miss doses.Q: Are there specific storage requirements for Bracanat 100 Mg Tablets?
A: Yes, store Bracanat 100 Mg Tablets below 30C, protecting them from light and moisture, and always keep them within their original packaging until use.Q: What possible side effects might occur while taking Bracanat 100 Mg Tablets?
A: Common side effects include nausea, fatigue, anemia, thrombocytopenia, constipation, and insomnia. If you experience severe or persistent symptoms, consult your physician promptly.Q: Who should not use Bracanat 100 Mg Tablets?
A: Bracanat 100 is contraindicated in individuals with hypersensitivity to Niraparib or its excipients. It should also be avoided during pregnancy and lactation unless specifically advised by a healthcare provider.Q: What are the benefits of using Bracanat 100 Mg in cancer treatment?
A: Bracanat 100 Mg acts as a PARP inhibitor, disrupting how cancer cells repair themselves. By inhibiting this process, it helps to control tumor growth and improve treatment outcomes in designated cancers.
Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+